Our greatest success is
Every grant obtained for our customers makes us proud.
It would be simply impossible to list all our projects here, but please feel invited to take a glimpse at a selection of our most important recent projects!


The European Commission (EC) aims to eliminate net greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions on the path to climate neutrality by mid-century. The transportation sector will play an important role in the transition to a society living on 100% renewable energy. Two key challenges towards achieving this target relate to (i) an increased feedstock basis for renewable fuel production and (ii) the long-term development of sustainable fuel technologies for aviation. While electrification, and likely also hydrogen, will play a major role in the decarbonization of transportation, there will still be a continued need for energy-dense liquid hydrocarbon fuels, especially for aviation and shipping. First-generation biofuels cannot meet the required volumes, due to availability and sustainability constraints. Hence, scalable technologies will be required to meet the longer-term fuel demand. Solar radiation is the most scalable form of renewable energy. SUN-to-LIQUID II will develop a set of versatile technologies for solar fuel production from water and CO2. The ultimate output will be a step-change technology advancement and a roadmap for a robust and sustainable conversion pathway to produce high-quality renewable liquid fuel from the inexhaustible potential of solar energy.
SUNlight-to-LIQUID – Efficient solar thermochemical synthesis of liquid hydrocarbon fuels using tailored porous-structured materials and heat recuperation
Acronym: SUN-to-LIQUID II
Runtime: 01/11/2023
Consortium: 6 partners
Funding programme: Horizon Europe (Lump Sum), 101122206
Total budget: 5.7 M€
Coordinator: Bauhaus Luftfahrt e.V. (Germany)
Website: https://sun-to-liquid-2.eu/



FITNESS aims to develop thin, flexible smart skins able to provide a non-contact sense of “touch”. The underlying key technology is that of meta-surfaces, i.e. structured surfaces that have unusual properties at some frequencies. The approach combines a variety of fields: RF front-end circuits, chemistry and polymer materials, flexible substrates, silicon integration, phased array antennas, metamaterials, numerical modelling, thermal management and communication systems.
The first demonstrator will be realised in the field of robotics, while later applications are envisaged in the medical area. One of the main societal outputs will be a more harmonious collaboration between robots and humans through the constant probing of their respective near-field environments.
Flexible IntelligenT Near-field Sensing Skins
Acronym: FITNESS
Runtime: 1 April 2023 to 31 March 2026
Consortium: 7 partners from 4 European countries
Funding programme: Horizon EIC Grant (Pathfinder programme), GA 101098996
Total budget: 3.6 M€
Coordinator: Université Catholique de Louvain (UCL), BE
Website: https://fitness-pathfinder.eu/



Achieving climate neutrality in Europe requires large volumes of sustainable fuels for transport sectors like aviation. The EU-funded CIRCULAIR project will design an integrated pathway that produces cost-effective aviation biofuels based on hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) of abundant agricultural residues. Key innovations of CIRCULAIR involve a close thermal coupling of HTL conversion with exothermic wet oxidation of the HTL process water. The project will also develop innovative approaches to upgrade HTL biocrudes to jet fuel and accelerate the approval of HTL fuels for civil aviation. Coupling with green hydrogen generation enables almost complete biomass utilisation and yields methanol as a main by-product. Furthermore, CIRCULAIR will close a knowledge gap regarding utilisation of HTL solids for soil amendment and carbon sequestration.
Circular fuel supply for air transport via negative emission HTL conversion
Acronym: CIRCULAIR
Runtime: 1 January 2023 to 31 December 2026
Consortium: 10 partners from 6 countries
Funding programme: Horizon Europe, grant agreement number 101083944
Total budget: 5 M€
Coordinator: Bauhaus Luftfahrt e.V. (Germany)
Website: https://www.project-circulair.eu/



Advanced composites are gaining ground in many areas, especially aerospace, automotive and renewable energy, as they are lightweight and help save energy. What is still missing are accurate and fast pre-production methods to optimise the durability of such large-scale composite structures. Therefore, D-STANDART aims to develop efficient methods for modelling the durability of large-scale composite structures of any design under realistic conditions.
Durability modelling of Composite Structures with arbitrary lay-up using standardised testing and artificial intelligence
Acronym: D-STANDART
Runtime: 1 January 2023 to 31 December 2025
Consortium: 9 partners from 4 countries
Funding programme: Horizon Europe, grant agreement number 101091409; UK Innovation and Research
Total budget: 5.6 M€
Coordinator: NLR │ Netherlands Aerospace Centre
Website: https://d-standart.eu/



The switch to hybrid-electric regional aircraft will represent a major step towards a climate-neutral aviation. As an enabler of the long-term vision of hybrid-electric regional aircraft by 2035, HECATE has the mission to develop new high-voltage electric power distribution technologies.
Hybrid-ElectriC regional Aircraft distribution Technologies
Acronym: HECATE
Runtime: 1 January 2023 to 31 December 2025
Consortium: 37 partners from 10 European countries
Funding programme: Clean Aviation (EU), UK Research and Innovation
Total budget: 53 M€
Coordinator: Collins Aerospace Ireland Ltd
Website: https://hecate-project.eu/



The EU faces an increasingly complex threat spectrum that requires very early warning systems. Especially hypersonic and ballistic threats call for a new and robust capability to complement existing assets. The EU-funded project "hIgh FreqUency oveR The Horizon sensors' cognitivE netwoRk" (iFURTHER) aims to develop a disruptive defence concept capable of protecting the sovereignty and integrity of the European Union.
High Frequency Over The Horizon Sensors’ Cognitive Network
Acronym: iFURTHER
Runtime: 1 December 2022 to 30 November 2025
Consortium: 18 partners from 10 countries
Funding programme: European Defence Fund (Lump Sum), grant agreement number 101103607
Total budget: 10.95 M€
Coordinator: Hellenic Aerospace Industry SA (Greece)
Website: No website



PATTERN will bring long-awaited breakthroughs in the field of Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) and provide unrivalled new functionalities for a vast range of applications. The project will devise the world’s first Process Design Kit (PDK) and Assembly Design Kit (ADK) for microwave photonics at ultra‐high frequencies above 100 GHz, new methods for heterogenous integration of III-v gain materials (e.g. InP), as well as BiCMOS drivers with an electro-optic and nonlinear platform of thin-film lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI). It will also develop new functionalities in PICs, such as acousto-optic modulation (AOM) and optical isolation capabilities. PATTERN’s impact will be showcased through several demonstrators, from quantum to satellite free-space communications to ultrastable optical-based RF sources. The results of PATTERN will be accessible to the photonics community in the form of an open-access foundry.
Next-Generation Ultra-High-Speed Photonics ICs via Heterogenous Integration of LNOI and InP Platforms
Acronym: PATTERN
Runtime: 1 Sept 2022 to 31 Aug 2026
Consortium: 10 partners from 6 countries
Funding programme: Horizon Europe, grant agreement number 101070506; UK Research and Innovation; SERI (Switzerland).
Total budget: 6.7 M€
Coordinator: THALES Research & Technology (France)
Website: www.pattern-project.eu


The ELENA project promises to benefit the entire photonics sector by developing the first European lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI)-based platform for photonic integrated circuits (PICs) and establishing the first open-access foundry service for LNOI technology.
European electro-optic and nonlinear PIC platform based on lithium niobate
Acronym: ELENA
Runtime: 1 January 2022 to 30 June 2025
Consortium: 10 partners from 3 countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 101016138
Total budget: 5 M€
Coordinator: CSEM │ Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology
Website: https://www.project-elena.eu/
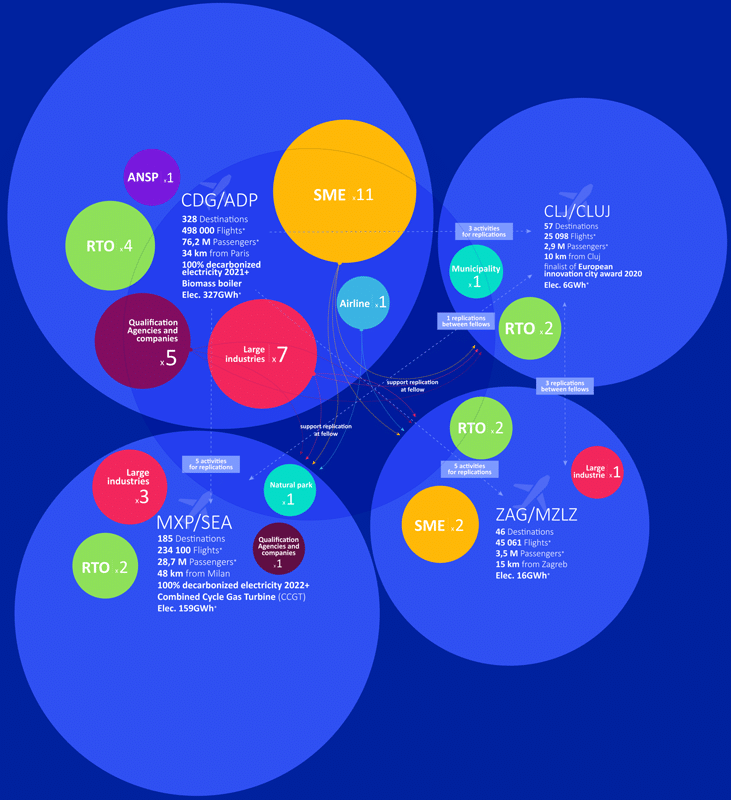


OLGA aims to boost the environmental performance of airports, thus facilitating the transition to low-carbon mobility and a climate-resilient society in line with the EU Green Deal.
OLGA is set to develop innovative sustainable measures to reduce both airside and landside emissions of airports with proven scalability and EU-wide applicability. Involving the entire value chain, OLGA strives to achieve CO2 and other GHG reduction, air quality improvement, biodiversity preservation, energy use reduction and sustainable construction concepts. Quantifiable advances are expected within the first three years already, thus accelerating the exploitation of results.
hOListic & Green Airports
Acronym: OLGA
Runtime: 1 Oct 2021 to 30 Sept 2026
Consortium: 42 partners from 9 EU countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 101036871
Total budget: 34 M€
Coordinator: AEROPORTS DE PARIS SA (ADP)
Website: https://www.olga-project.eu/



FIBRE4YARDS will contribute to maintaining the global competitiveness of small and medium European shipyards. The objective is to develop an innovative cost-efficient, digitized, automated and modular vessel production approach using Fibre Reinforced Plastic and advanced production technologies (adaptive moulds, ATP/AFP, 3D printing, curved pultrusion profiles, hot stamping, innovative composite connections) from other industrial sectors, and to adapt and combine them in a “shipyard 4.0” environment.
Compliance with the regulatory framework and the necessary training to upskill production teams will be ensured; all within validated and viable business models targeting a circular and resource-efficient maritime sector (less fuel consumption, recyclable materials, energy-efficient production, less noise pollution).
Fibre Composite Manufacturing Technologies for the Automation and Modular Construction in Shipyards
Acronym: Fibre4Yards
Runtime: 1 Jan 2021 to 31 Dec 2023
Consortium: 13 partners from 6 EU countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 101006860
Total budget: 7.5 M€
Coordinator: CIMNE (ES)
Website: https://www.fibre4yards.eu/



To meet the goal of a carbon-neutral growth of commercial aviation, the top-level objective of IMOTHEP is to achieve a key step in assessing the potential offered by hybrid-electric propulsion and, ultimately, to build a corresponding sector-wide roadmap for the maturation of the technology.
The core of IMOTHEP is an integrated end-to-end investigation of hybrid-electric power trains for commercial aircraft, performed in close connection with the propulsion system and aircraft architecture. Aircraft configurations will be selected based on their potential for fuel burn reduction and their representativeness of a variety of credible concepts, with a focus on regional and short-to-medium range missions.
Investigation and Maturation of Technologies for Hybrid-Electric Propulsion
Acronym: IMOTHEP
Runtime: 1 Jan 2020 to 31 Dec 2023
Consortium: 34 partners from 11 countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 875006
Total budget: 18.35 M€
Coordinator: ONERA / Office National d’Etudes et de Recherches Aérospatiales (France)
Website: https://www.imothep-project.eu/



The European-Chinese Research and Innovation project GreAT seeks to reduce aviation's impact on climate change across continents.
The consortium investigates new possibilities to manage air traffic in a greener way. Optimised flight trajectories will help to reduce fuel consumption during all flight phases, for instance through optimisation of airspace design and controller support tools.
GreAT also considers increasingly challenging and conflicting factors, such as the constant growth of air traffic, but also more complex items such as the environment, weather, aircraft operations and maintenance.
Greener Air Traffic Operations
Acronym: GreAT
Runtime: 1 Jan 2020 to 30 June 2023
Consortium: 13 partners from 6 EU countries and China
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 875154
Total budget: 6.99 M€
Coordinator: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR) / German Aerospace Center (DE)
Website: https://www.project-great.eu/



Europe’s photovoltaics manufacturing industry is facing strong foreign competition. The HIPERION project is working on enabling mass production of a new disruptive technology that concentrates sunlight on multijunction solar cells and can be mounted on top of a conventional silicon backplate. A game-changer, this high-efficiency module-level innovation has proven its performance in extensive outdoor tests and pilot installations. The focus now is on enabling its integration by manufacturers.
The project is led by a consortium of 16 members and includes industrial players with key expertise. A solar manufacturer will conduct a detailed financial evaluation on technology integration in the production line, while several solar installers will represent both the rooftop and utility end markets.
Hybrid Photovoltaics for Efficiency Record Using Integrated Optical Technology
Acronym: HIPERION
Runtime: 1 Sept 2019 to 31 Aug 2023
Consortium: 16 partners from 10 countries (8 EU plus Switzerland and United Kingdom)
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 857775
Total budget: 13.53 M€
Coordinator: CSEM (Switzerland)
Website: https://hiperion-project.eu/



The LEMON project aims at developing a Lidar emitter for space applications to monitor greenhouse gases and water vapour. LEMON will improve the accuracy of climate change analysis.
Based on innovative photonics components, LEMON will develop a cutting-edge Differential Absorption Lidar (DIAL) sensor concept that can either measure CO2, CH4 or water vapour stable isotopes in a rugged and compact architecture that matches mini-satellite missions size requirements.
Lidar Emitter and Multispecies greenhouse gases Observation instrument
Acronym: LEMON
Runtime: 1 Jan 2019 to 30 June 2023
Consortium: 8 partners from 4 countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 821868
Total budget: 3.56 M €
Coordinator: Office National d'etudes et de recherches aerospatiales
Website: https://lemon-dial-project.eu/


Modern aircraft are well equipped to cope with the most common icing conditions. However, some conditions, especially involving so-called “Supercooled Large Droplets”, have been the cause of severe accidents. Thus, improving safety in these icing conditions is important.
The SENS4ICE project directly addresses the need for reliable detection of icing conditions and introduces a novel approach of hybridisation of different detection techniques: In the proposed hybrid system, the direct sensing of atmospheric conditions and/or ice accretion on the airframe is combined with an indirect detection of ice accretion on the airframe by monitoring the change of aircraft’s characteristics.
Sensors and Certifiable Hybrid Architectures for Safer Aviation in Icing Environment
Acronym: SENS4ICE
Runtime: 1 Jan 2019 to 31 Dec 2022
Consortium: 20 partners from 6 EU countries plus Brazil, Canada, United Kingdom, Russia, and US
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 824253
Total budget: 12 M€
Coordinator: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR) / German Aerospace Center (DE)
Website: http://www.sens4ice-project.eu/



Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) enable substituting traditional building materials with high-quality architectural designs and contribute to reducing CO2 emissions. BIPV will contribute to significant clean electricity generation in line with EU policy, and the rebuilding of a more robust European solar energy industry. Presently, BIPV use is primarily limited to symbolic façade and rooftop demonstration projects, often with standard modules mounted on the surface of existing buildings. This project will help remove barriers that have - so far - hindered BIPV implementation by supporting the industrialisation of new multifunctional BIPV elements and focusing on cost-effective, breakthrough transformative approaches to achieve aesthetic modules.
BE-Smart: Innovative Building Envelope for Sustainable, Modular, Aesthetic, Reliable and Efficient Construction
Acronym: Be-Smart
Runtime: 1 Oct 2018 to 30 Sep 2022
Consortium: 15 partners from 9 countries
Funding programme: Horizon 2020, grant agreement number 818009
Total budget: 8.16 M€
Coordinator: ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (Switzerland)
Website: https://www.besmartproject.eu/



The SuCoHS project investigates potential weight and cost savings in expanding the use of composite materials in aeronautic components. The aim is to conceive novel multi-material composites providing high resistivity against thermal (high temperatures, fire) as well as mechanical loading, allowing for cost-competitive manufacturing while reducing the requirement for visual inspection or rework. New solutions for structural health monitoring are considered to enable condition-based maintenance.
The project will develop a framework to adapt these promising technologies to different aeronautic components. Three industrial use cases are defined to set requirements, validate new technologies and demonstrate technical feasibility: a high-temperature resistance nacelle component, a composite aircraft interior shell and a tail cone panel substructure.
Sustainable and Cost-Efficient High-Performance Composite Structures Demanding Temperature and Fire Resistance
Acronym: SuCoHS
Runtime: 1 Sept 2018 to 28 Feb 2022
Consortium: 14 partners from 6 EU countries and Switzerland
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 769178
Total budget: 6.64 M€
Coordinator: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR) / German Aerospace Center
Website: https://www.sucohs-project.eu/



The MADELEINE project focuses on the development and validation of multidisciplinary design tools for optimisation. Special attention is given to multidisciplinary optimisation, to the understanding of multi-physics phenomena, to the simulation of manufacturing processes, and the transition to High-Performance Computing (HPC). During aircraft or engine design, most optimisation studies using high-fidelity tools are focused on a single discipline (such as aerodynamics, acoustics, heat transfer or structural analysis).
This single-disciplinary approach prolongs the overall process and makes it difficult to exploit multi-discipline trade-offs.
The MADELEINE consortium is working on a new design tool that meets the industrial need of competitiveness and fosters the integration of greener technologies.
Multidisciplinary Adjoint-Based Enablers for Large-Scale Industrial Design in Aeronautics
Acronym: MADELEINE
Runtime: 1 June 2018 to 30 November 2021
Consortium: 15 partners from 5 EU countries plus United Kingdom
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 769025
Total budget: 5.81 M€
Coordinator: Onera / Office National d’Etudes et de Recherches Aeriospatiales (France)
Website: https://www.madeleine-project.eu/



The goal of the ACASIAS project (completed in 2020) was to develop advanced concepts for aerostructures with multifunctional capabilities by embedding sensors and antennas into typical aircraft structures (such as fuselage panels, winglets, tails), enabling to reduce CO2 and NOx emissions, overall airframe weight, cabin noise due to CROR engines, as well as maintenance costs.
The innovative technologies developed within ACASIAS relate to antenna design, composite manufacturing process, radiofrequency, and structural analysis.
Advanced Concepts for Aero-Structures with Integrated Antennas and Sensors
Acronym: ACASIAS
Runtime: 1 June 2017 to 31 May 2020
Consortium: 11 partners from 6 countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 641864
Total budget: 5.84 M€
Coordinator: Stichting Nationaal Lucht- en Ruimtevaartlaboratorium (NL)
Website: http://www.acasias-project.eu/



MINOTOR’s (completed 2020) strategic objective was to demonstrate the feasibility of the ECRA (Electron Cyclotron Resonance Accelerator) technology as a disruptive game-changer in electric propulsion.
The project represents a significant step in maturing the ECRA technology from TRL3 to TRL4/5 and will help assess its potential to improve European competitiveness, help develop low-cost satellite solutions for constellation management, including end-of-life propulsion, while paving the way for other future emerging electric propulsion technologies.
Magnetic Nozzle Thruster with Electron Cyclotron Resonance
Acronym: MINOTOR
Runtime: 1 June 2017 to 31 July 2020
Consortium: 7 partners; 4 from EU countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 730028
Total budget: 1.49 M€
Coordinator: Onera / Office National d’Etudes et de Recherches Aeriospatiales (France)
Website: http://www.minotor-project.eu/



The main objective of the cooperation of the Chinese and European partners in ECO-COMPASS (completed in 2019) was to develop and assess multifunctional and ecologically improved composites from bio-sourced and recycled materials for application in aircraft secondary structures and interior.
Therefore, bio-based reinforcements, resins and sandwich cores were developed and optimized for their application in aviation.
A cradle-to-grave Life Cycle Assessment enabled the comparison of the new eco-composites with state-of-the-art materials.
Ecological and Multifunctional Composites for Application in Aircraft Interior and Secondary Structures
Acronym: ECO-COMPASS
Runtime: 1 April 2016 to 30 June 2019
Consortium: 8 partners from EU countries plus China
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 690638
Total budget: 1.89 M€
Coordinator: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR) / German Aerospace Center (DE)
Website: http://www.eco-compass.eu/



AIRMES (completed in 2019) focused on reducing technically induced operational disruptions in European air traffic by optimising end-to-end maintenance activities within an operator’s environment.
The consortium developed an innovative maintenance service architecture that reduces the average delay time and improves aircraft utilisation.
This represents a key step in achieving zero flight delays due to direct aircraft technical causes and consequential delays on subsequent flights. The overall business benefit of this project is estimated at around one billion €.
Airline Maintenance Operations Implementation of an E2E Maintenance Service Architecture and Its Enablers
Acronym: AIRMES
Runtime: 1 Dec 2015 to 30 Nov 2019
Consortium: 12 partners from 6 countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 611858
Total budget: 5.19 M €
Coordinator: TAP (Portugal)
Website: https://www.airmes-project.eu/



INREP’s (concluded in 2018) objective was to develop and deploy valid and robust indium-free transparent conducting oxides (TCOs) to replace indium-based conductive electrode materials in applications such as high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, GaN-based LEDs, organic LEDs, and touchscreen monitors.
The physical properties of interest were transparency, electrical conductivity, work function, texture, as well as chemical and thermal stability.
Towards Indium-free TCOs
Acronym: INREP
Runtime: 1 Feb 2015 to 31 Jan 2018
Consortium: 13 partners from 7 EU countries
Funding programme: H2020, grant agreement number 641864
Total budget: 6.20 M€
Coordinator: University of Bath (UK)
Website: http://www.inrep.eu/



AFLoNext (completed in 2018) was a four-year EC L2 project with the objective of proving and maturing highly promising flow control technologies for novel aircraft configurations to achieve a quantum leap in improving aircraft’s performance and thus reducing the environmental impact.
This large project was performed by a consortium of forty partners from fifteen countries.
"2nd Generation Active Wing“ – Active Flow-Loads & Noise Control on Next Generation Wing
Acronym: AFLoNext
Runtime: 1 June 2013 to 31 May 2017
Consortium: 40 partners from 15 countries (12 EU countries, United Kingdom, Israel, Russia)
Funding programme: FP7, grant agreement number 604013
Total budget: 37.16 M€
Coordinator: AIRBUS OPERATIONS GmbH (Germany)
Website: http://www.aflonext.eu/
